
Module 1 — Effective
writing: Strategies
and principles
| Course Guide | Module 1 | Module 2a | Module 2b |
Prewriting techniques
The following techniques explore methods you can use to help you produce a first draft quickly, avoid writer’s block and clarify your thoughts. Try some or all of these early on in the writing.
Brainstorming
Write down all the ideas you have about your writing task. You can do this on paper or directly onto your computer. If you prefer to speak while you’re brainstorming, you can even record brainstorming ideas on your voice mail!
While brainstorming:
- do not cross out or delete any ideas or words;
- do not worry about spelling or finding the correct words;
- do not allow anything to interrupt your flow of thought;
- do not evaluate or criticize any aspect of your writing.
The following techniques are really variations on the theme of brainstorming.
The random list
List everything that comes to mind and then sort it into groups. Look for connections: sequential, spatial, chronological, topical, pros and cons, etc.
FCR
This technique is useful if your topic requires a solution. Divide your page into three headings: findings (F), conclusions (C), and recommendations (R). List your ideas in these three categories.
Journalistic approach
Useful if your task is to convey information. Ask and answer six questions:
- Who?
- What?
- When?
- Where?
- Why?
- How?
Question and answer chain
Look at the subject from your readers' perspective. Put yourself in your readers' position by asking:
- What are my readers' main questions likely to be?
- What do they need to know?
Examine your answers to these questions. What additional questions emerge? Follow the question and answer chain until you have exhausted all questions.
Free writing
Set yourself a limited time for free writing: say five minutes for a task like a letter. Just write without worrying about grammar, spelling, sentences, structure or anything else. If you get stuck, repeat the last words you have written until new thoughts start to come.
Whichever brainstorming approach you take, the end result will be similar. Instead of a blank piece of paper, you will now have a list or several paragraphs containing many of the ideas you want to include in the document you are writing.
Outlining your ideas
One of the most efficient ways to brainstorm is to use the Outline facility (under View menu) in Microsoft Word. It provides an excellent tool for efficient brainstorming, and helps you get the writing task itself started in the process.
The Outline facility in Word allows you to work in a way that suits you best. You can use the Outline facility to:
- build your plan;
- reorder information;
- change headings; or
- add to or delete from the plan at any stage.
One of its advantages is that whatever work you do in the Outline view will immediately appear in your document; you are not wasting any effort at all. Outline lets you work in any part of the document in any order you choose.
Levels of headings
The Outline facility operates on the idea of levels of headings. For writing of any length (for example, reports), the concept of levels of headings (main headings, sub-headings, sub-sub-headings etc) is extremely important and will be explored more fully in the Report Writing module. For now, you might like to try Outline next time you have a major writing task. You will find it under the VIEW pull-down menu or you may have it on your toolbar as an icon. Your screen may be a little different from the one below, depending on the version of Word that you are using.
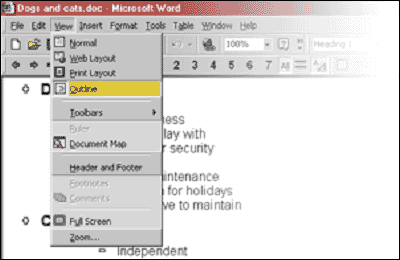
If you are unfamiliar with this facility, you will find it useful to read the appropriate sections in the HELP menu.